ACQUIRED DIGITAL FIBROKERATOMA
Luciano Schiazza M.D.
Dermatologist
c/o InMedica - Centro Medico Polispecialistico
Largo XII Ottobre 62
cell 335.655.97.70 - office 010 5701818
www.lucianoschiazza.it
Acquired digital fibrokeratoma (ADFK) is a benign lesion that typically occurs on the fingers or toes of adult.
The name was coined in 1968 from Bart et al. describing a benign acquired projection on the digits.
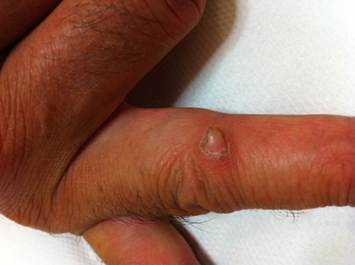
ADFK clinically appears as a solitary, non-painful or itchy, well-circumscribed. Skin colored or pink dome-shaped papule or fingerlike protrusion. Rarely exceeds 1.5 centimeters in height or diameter. Around the base if growth there is a collarette of raised scaly skin which which is a diagnostic feature.
The most common histopathologic finding in ADFK includes an acanthotic hyperkeratotic epidermis which envelope a core of connective tissue showing interwoven bundles of collagen predominantly oriented along the vertical apex of the lesion. There is also an increase in the vascularity, number of fibroblasts and vessels between collagen bundles.
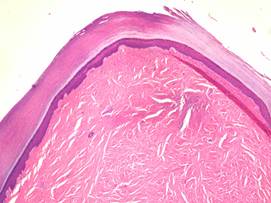
The pathogenesis of ADFK is not currently known: a traumatic cause is favored by some, despite the fact that mostt patients deny a history of precedent trauma. The major hypothesis is that subclinical injury contributes to the development of ADFK as a promoting factor.
The differential diagnosis of ADFK includes a rudimentary supernumerary digit, knuckle pad, sclerotic fibroma, dermatofibroma. All these lesions may be differentiated clinically. A characteristic of ADFK is the presence of a collarette of slightly raised skin or of scale encircling the lesion.
It does not show spontaneous regression. Surgical excision is the treatment of choice.
