Dengue
Luciano Schiazza M.D.
Dermatologist
c/o InMedica - Centro Medico Polispecialistico
Largo XII Ottobre 62
cell 335.655.97.70 - office 010 5701818
www.lucianoschiazza.it
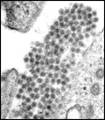
Dengue is a viral disease, caused by four closely related virus serotypes of the genus Flavivirus (DEN-1, DEN-2, DEN-3, DEN-4), family Togaviridae. Each sierotype is sufficiently different and there is no cross-protection : so it’s possible a secondary infection by a different dengue virus serotype.

Dengue is transmitted to humans by the Aedes aegypty (rarely Aedes albopictus) mosquito, which feeds during the day. The mosquito can tranmit the virus eight-ten hours after the infected meal.
There is no direct man to man contagion, unless through contact with infected blood. It is said that a subject is contagious within six days from the insurgence of the disease.
Epidemics are spread in tropical and sub-tropical areas, within the 35th latidute North and 35th latitude South (over 100 Countries).
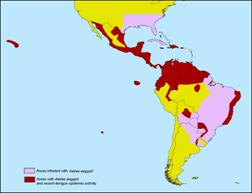
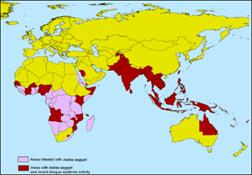
60 to 100 milion cases per year, included 500,000 cases affected by DSS (dengue shock syndrome) and 20,000 deaths.
Dengue spreads mainly in large urban areas, slums, strong demographic growth areas where most likely you can find stagnant water and sewage. In such a context the possibility to contract the diseases increases dramatically because it is the perfect breeding habitat for the mosquitos.
Aedes aegypty breeds primarily in man-made containers such as jars, metal drums and concrete cysterns used for domestic water storage, as well as discarted plastic food containers, used automobile tyres and other items that collect rainwater. In Africa it also breeds extensively in natural habitats such as tree holes and leat axils.
The rapid international trade is responsible of the spread of the disease.
Common dengue,or dengue fever is a severe flu-like illness that affects infants, young children and adults, but seldom causes death.
Incubation period: 2 – 7 days.
Symptoms:
-
Sudden high fever (39°-40° C) (104° F), shivers
-
Headache
-
Myalgias (Muscle aches)
-
Arthralgias (Severe joint pain) (gives it the name of « fever break-bone »)
-
Retro-horbital pain. (pain behind the eyes)
-
Rashes. The dengue rash is characteristically bright red and usually appears first in the lower limbs and the chest (sparing palms and soles), in first 1-2 days of fever ; in some patients it spreads to cover most of the body. It usually lasts 3-4 days and leaves itch and desquamation for a few weeks.
-
Leukopenia (abnormally low white blood cells)
After 3-4 days there is a short remission of the symptoms, there is a second recurrence (so called « biphasic pattern ») with a morbilliform, maculopapular rash symphoms such as :
-
conjunctiva's hemorrhages
-
nasal bleeding
-
ecchymoses that last for about a week
The classic dengue fever lasts about 9 to 14 days with asthenia. Although severe, it is not life threatening.
A second dengue infection with a different dengue serotype in people who are actively or passively (from mother) immunized to one of the dengue virus, is an important risk factor to develop a disseminated intravascular coagulation, the dengue hemorrhagic fever(DHF). 20-30% of DHF patients can develop shock known as dengue shock syndrome(DSS).
Different is the course of DHF and DSS instead classic dengue fever. The mortality, or death rate, with DHF/DSS is significant. It ranges from 6% (treated cases) to 50% (untreated cases). Most deaths occur in children. Infants younger a year of age are especially at risk of dying from DHF.
Dengue hemorrhagic fever is characterized by::
-
No bone pain
-
Severe abdominal pain
-
Gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding
-
Gum bleeding
-
Petecchiae, purpura (blood spots in the skin)
-
Cerebral hemorrhage
-
Thrombocytopenia (1000 platelets per mm³ or estimated as less)
-
Hematocrit increased 20% (hemoconcentration)
-
Leukopenia
-
Elevated transaminases
-
Hypoproteinemia
-
Elevated BUN
-
Hepatomegaly (enlarged liver)
-
Generalized lymphadenopathy
The evolution of DHF, after 5 – 7 days can follow two paths:
-
Decrease of fever through lysis, regression of the symptoms and recovery within 10-12 days.
-
DSS, due to the serious haemorragyc, which leads to:
-
Weak rapid pulse,
-
Hypotension with narrow pulse pressure (less than 20 mm Hg)
-
Cold, clammy skin
-
Restlessness
-
DSS may bring death within 12-24 hours, in absence of medical treatment. At major risk are children and weak people.
A guaiac test for occult bloodin the stool should be performed in a patient in whom dengue fever is suspected, because a positive test can be an early sign of coagulopathy.
There is no specific treatment, or vaccine for dengue fever, and most people recover within 2 weeks. To help with recovery, health care experts recommend:
-
Getting plenty of bed rest
-
Drinking lots of fluids
-
Taking medicine to reduce fever
Prevention consists essentially in avoiding mosquito bites, knowing that they are more active during the day (the tow hours preceding sunrise and the two hours preceding sunset). Mosquitos might also bite during the night in lightened areas.
It is therefore necessary to:
-
wear long sleeves and long trousers in light colors
-
use repellents in uncovered areas of the body
-
use mosquito nets impregneted with pyrethrin
-
applying repellents after swimming
Getting rid of areas where mosquitos breed, such as standing water in flower pots, containers, birdbaths, discarded tyres, etc.
